Pro-Infliximab provided equivalent therapeutic efficacy to Infliximab while maintaining mouse immunity against Listeria infection, leading to a significantly higher survival rate (71%) than that of the Infliximab treatment group (0%).
Published in PLoS Biology 2019 Jun 13;17(6):e3000286. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000286.
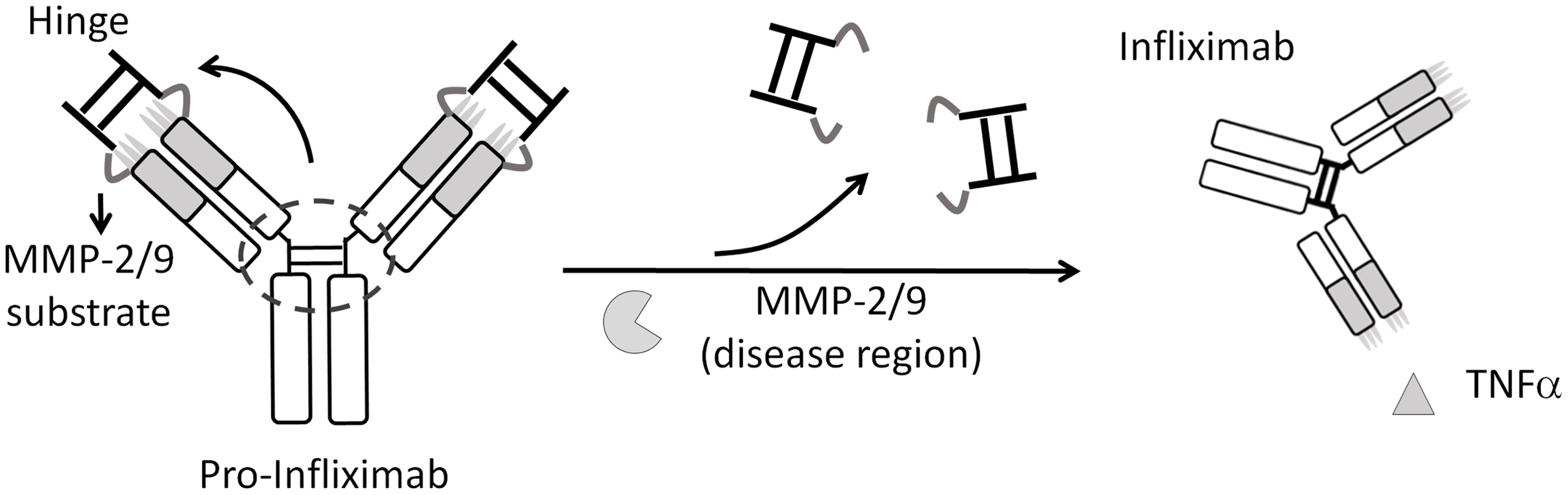
Specific activation of pro-Infliximab enhances selectivity and safety of rheumatoid arthritis therapy
During rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment, long-term injection of antitumor necrosis factor α antibodies (anti-TNFα Abs) may induce on-target toxicities, including severe infections (tuberculosis [TB] or septic arthritis) and malignancy. Here, we used an immunoglobulin
G1 (IgG1) hinge as an Ab lock to cover the TNFα-binding site of Infliximab by linking it with matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) -2/9 substrate to generate pro-Infliximab that can be specif- ically activated in the RA region to enhance the selectivity and safety of treatment. The Ab lock significantly inhibits the TNFα binding and reduces the anti-idiotypic (anti-Id) Ab binding to pro-Infliximab by 395-fold, 108-fold compared with Infliximab, respectively, and MMP-2/9 can completely restore the TNFα neutralizing ability of pro-Infliximab to block TNFα down- stream signaling. Pro-Infliximab was only selectively activated in the disease site (mouse paws) and presented similar pharmacokinetics (PKs) and bio-distribution to Infliximab. Fur- thermore, pro-Infliximab not only provided equivalent therapeutic efficacy to Infliximab but also maintained mouse immunity against Listeria infection in the RA mouse model, leading to a significantly higher survival rate (71%) than that of the Infliximab treatment group (0%). The high-selectivity pro-Infliximab maintains host immunity and keeps the original therapeu- tic efficiency, providing a novel strategy for RA therapy.